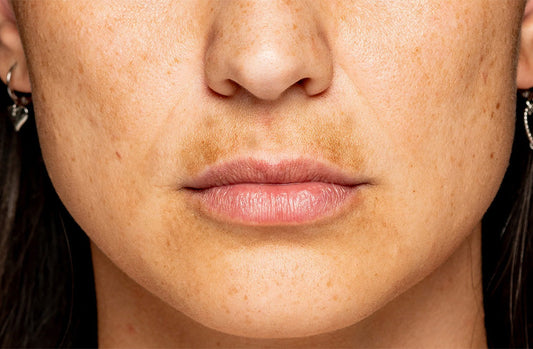
Hyperpigmentation
-

Works with even the most sensitive skin to improve dull, stressed skin tone and texture
without irritation and drying. -

Customized by a board certified dermatologist using medical-grade ingredients proven to be effective for skin discoloration.
-

Developed to minimize dark spots from hyperpigmentation and melasma without synthetic fragrance or harsh chemicals.
-

The Plus Program
15% off 2 products
20% off 3 or more
Create your regimen!
No sign up required.
Discount automatically applied.Subscriptions not included.
-
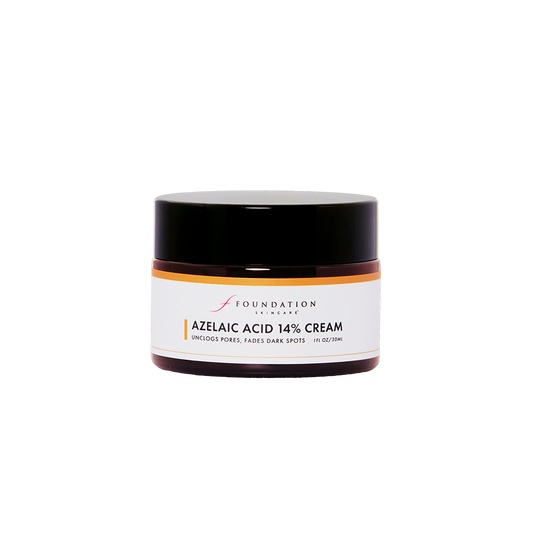

Azelaic Acid 14% Cream Subscription Available
• Reduces acne & rosacea
• Brightens skin, fades brown spots
• Unclogs pores, improves textureSee detailsRegular price $45Regular priceUnit price per -

Niacinamide Lotion 10% Subscription Available
• Renews dry, dull skin and texture
• Helps retain moisture and elasticity
• Reduces inflammation & rednessSee detailsRegular price $45Regular priceUnit price per -

Night Renewal Cream Subscription Available
• With 2% Granactive Retinoid
• Anti-aging defense, moisturizer
• Improves fine lines, skin textureSee detailsRegular price $45Regular priceUnit price per -

Vitamin C Lotion 20% Subscription Available
• Exfoliates dead cells to improve skin tone
• Increased collagen production renews skin
• Antioxidant power repairs discolorationSee detailsRegular price $45Regular priceUnit price per -
-
“Really notice a BIG difference in my skin tone, and a HUGE difference in my melasma.
My skin looks so much more radiant in only 2 weeks. I’ve used SO many different
and more expensive products, and they did not work as well. PLEASE continue to offer
your amazing products at a reasonable price for all.”– Melissa R. Verified Buyer
★★★★★
Both internal and external
influences cause discoloration
in a range of skin types.




-

-
A daily routine of
targeted ingredients
can help significantly
improve melasma and
hyperpigmentation.
-
Exfoliating properties and an ability to inhibit melanin production work to even skin tone.
SHOP HYPERPIGMENTATION -
- Dermatologist + chemist formulated
- Proven ingredients for hyperpigmentation >
- Layers well without being sticky or pilling
- Not irritating or drying, gentle for daily use
- Improves skin brightness and texture
- See our money back guarantee >
- Dermatologist + chemist formulated
Collapsible content
What do dermatologists recommend for hyperpigmentation?
The first and foremost is sunscreen. Physical sunscreens with zinc and or titanium are paramount in preventing the pigmentation from getting worse. Tinted sunscreens also contain iron oxide which provides additional benefit.
Treatment for pigmentation is one of the biggest markets in skincare. Lasers and chemical peels are often employed for more serious cases of hyperpigmentation. At home prescriptions are typically made by compounding pharmacies and include various permutations of the Kligman Formula (a cream with combinations of hydroquinone, a steroid and a retinoid). While often effective, this combo can have irritation and side effects including a permanent type of pigmentation called ochronosis when used too long. Oral tranexamic acid is effective for severe cases of melasma but should always be done under the supervision of a board certified dermatologist who can discuss the risks.
Better options for hyperpigmentation are the following topicals, in addition to daily sunscreen use:
• Azelaic Acid – Known for its ability to calm inflammation and gently reduce excess pigment without irritating the skin.
• Niacinamide (Vitamin B3) – Helps even skin tone by minimizing pigment transfer while strengthening the skin barrier.
• Vitamin C and retinoids – also common, though they can be sensitizing for some skin types.
• Dermatologists also recommend oral supplements with polypodium, alpha lipoic acid and various other vitamins to help with melasma.
Why hydroquinone is NOT recommended?
Hydroquinone has long been used to treat stubborn hyperpigmentation – but it comes with important considerations. While effective for some, it can cause irritation, rebound pigmentation, and in rare cases, long-term skin damage like ochronosis (a near permanent blue black pigmentation). This is more likely to occur in preparations over 4% hydroquinone used for long periods of time. Hydroquinone is also melanotoxic – meaning in addition to reducing the pigment produced it actually kills the pigment producing cells themselves. This melanotoxicity is part of what makes hydroquinone effective in the short term. However, it also raises safety concerns with long-term use, especially among people with darker skin tones who are at increased risk for rebound hyperpigmentation or exogenous ochronosis (a bluish-black skin discoloration). For this reason, many dermatologists prefer non-toxic alternatives – like azelaic acid, which inhibits tyrosinase without killing melanocytes, offering a safer, long-term approach to managing pigmentation.
A variant of hydroquinone, monobenzyl ether of hydroquinone, is actually used to chemically induce vitiligo and kill all of the pigment cells in some patients with extreme disease who want all of their skin the same color.
That’s why many skincare experts and dermatologists now recommend safer, long-term solutions that are not melanotoxic – like azelaic acid and niacinamide – for fading discoloration. These ingredients offer gentle, sustained results with less risk and are suitable for a wider range of skin tones and sensitivities.
What does skin hyperpigmentation look like?
Hyperpigmentation is caused by an increase in melanin in the skin. Hyperpigmentation can look like patches of your skin appearing darker than the surrounding skin. This can appear as age spots, melasma, and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation.
What causes hyperpigmentation?
The cause of hyperpigmentation depends on the type. Some include genetics, hormone changes, melasma, medications, medical conditions like Addison’s disease and sun damage. A doctor or dermatologist can typically identify the type and cause of hyperpigmentation.
Are there different types of hyperpigmentation?
There are many different types of hyperpigmentation. The most common are melasma, age spots, and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation.
Can hyperpigmentation be prevented?
It is not always possible to prevent hyperpigmentation or stop it from becoming more noticeable, but there are some ways to reduce the risk. You can protect your skin by using sunscreen with SPF 30 or above, avoiding picking skin after an injury, taking recommended vitamins, and using dermatologist-recommended skincare products like niacinamide, vitamin C and azelaic acid.